Protilátky ke tkáňové transglutamináze
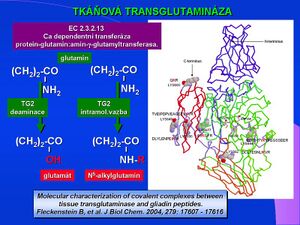
Anti-tTG IgA, IgG (atTg) jsou protilátky ke tkáňové transglutamináze. Tkáňová transglutamináza má přímý vztah k patogenezi onemocnění a byla popsána jako vlastní, chemický substrát endomysia. Tkáňová transglutamináza (izoenzym transglutamináza II, TG2 – EC 2.3.2.13), je transferázou, systémový název je protein-glutamin:amin-γ-glutamyltransferasa. Je to Ca2+ dependentní enzym katalyzující deaminaci glutaminu na glutamát, rovněž vede ke vzniku intramolekulární vazby glutaminu na další primární amin, např. lysin, a vede k agregaci glutaminových peptidů. Stanovení protilátek ke tkáňové transglutamináze (atTG) má proto rovněž velmi vysokou diagnostickou efektivitu, podobně jako protilátky proti endomysiu (senzitivita 87–97 % a specificita 88–98 %).
Stanovení atTG je prováděno klasickou metodou ELISA, což je pro rutinní diagnostiku technika dostupnější než imunofluorescenční průkaz protilátek proti endomysiu (EmA).
Protilátky atTG lze na rozdíl od EmA stanovovat ve třídě IgA i IgG, což má význam pro nemocné se selektivním deficitem IgA. Metoda byla popsána s použitím antigenu morčete, který je použit ve většině starších souprav. Novější soupravy již používají jako antigen tkáňovou transglutaminázu izolovanou z lidských buněk, z lidských erytrocytů, nebo rekombinantní tTG izolovanou na E. coli. Referenční hodnoty se liší u jednotlivých souprav, většinou je pro IgA protilátky uváděna horní hranice normy 10–15 IU/l, některé soupravy definují i tzv. šedou zónu (gray-zone) v rozsahu 10–20 IU/l. Stanovení protilátek atTG s lidským rekombinantním antigenem vykazuje nižší falešnou pozitivitu než metody s antigenem morčete. Nejnovější studie porovnávají protilátky třídy IgA a IgG a POCT metodiky stanovení atTG protilátek.
Stanovení protilátek atTG ve třídě IgA je doporučeno jako základní screeningový test pro diagnostiku céliakie.
Odkazy[upravit | editovat zdroj]
Zdroj[upravit | editovat zdroj]
- se svolením autora převzato z KOCNA, Petr. GastroLab : MiniEncyklopedie laboratorních metod v gastroenterologii [online]. ©2002. Poslední revize 2011-01-08, [cit. 2011-03-04]. <http://www1.lf1.cuni.cz/~kocna/glab/glency1.htm>.
Použitá literatura[upravit | editovat zdroj]
- BAVIERA, LC, et al. Celiac disease screening by immunochromatographic visual assays: results of a multicenter study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007, vol. 45, no. 5, s. 546-50, ISSN 0277-2116 (Print), 1536-4801 (Electronic). PMID: 18030231.
- SÁRDY, M, et al. Tissue transglutaminase ELISA positivity in autoimmune disease independent of gluten-sensitive disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2007, vol. 376, no. 1-2, s. 126-35, ISSN 0009-8981 (Print), 1873-3492 (Electronic). PMID: 16987503.
- BYRNE, G, et al. Mutagenesis of the catalytic triad of tissue transglutaminase abrogates coeliac disease serum IgA autoantibody binding. Gut. 2006, vol. 56, no. 3, s. 336-41, ISSN 0017-5749 (Print), 1468-3288 (Electronic). PMID: 16935926.
- RAIVIO, T, et al. Self transglutaminase-based rapid coeliac disease antibody detection by a lateral flow method. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006, vol. 24, no. 1, s. 147-54, ISSN 0269-2813 (Print), 1365-2036 (Electronic). PMID: 16803613.
- BARKER, CC, et al. Can tissue transglutaminase antibody titers replace small-bowel biopsy to diagnose celiac disease in select pediatric populations?. Pediatrics. 2005, vol. 115, no. 5, s. 1341-6, ISSN 0031-4005 (Print), 1098-4275 (Electronic). PMID: 15867045.
- MANKAÏ, A, et al. Tissue transglutaminase antibodies in celiac disease, comparison of an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay and a dot blot assay. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2005, vol. 53, no. 4, s. 204-9, ISSN 0369-8114 (Print), 1768-3114 (Electronic). PMID: 15850953.
- BAUDON, JJ, et al. Diagnosing celiac disease: a comparison of human tissue transglutaminase antibodies with antigliadin and antiendomysium antibodies. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004, vol. 158, no. 6, s. 584-8, ISSN 1072-4710 (Print), 1538-3628 (Electronic). PMID: 15184223.
- FERRE-LÓPEZ, S, et al. Immunochromatographic sticks for tissue transglutaminase and antigliadin antibody screening in celiac disease.. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004, vol. 2, no. 6, s. 480-4, ISSN 1542-3565 (Print), 1542-7714 (Electronic). PMID: 15181616.
- Tommasini A. - Arch Dis Child. 2004, 15155392. Mass screening for coeliac disease using antihuman transglutaminase antibody assay. Arch Dis Child. 2004, vol. 89, no. 6, s. 512-5, ISSN 0003-9888 (Print), 1468-2044 (Electronic). PMID: 15155392.
- SINCLAIR, D, et al. A comparative study of tissue transglutaminase antibodies and endomysium antibody immunofluorescence in routine clinical laboratory practice. Ann Clin Biochem. 2003, vol. 40, s. 411-6, ISSN 0004-5632 (Print), 1758-1001 (Electronic). PMID: 12880544.
- TONUTTI, E, et al. The role of antitissue transglutaminase assay for the diagnosis and monitoring of coeliac disease: a French-Italian multicentre study. J Clin Pathol. 2003, vol. 56, no. 5, s. 389-93, ISSN 0021-9746 (Print), 1472-4146 (Electronic). PMID: 12719462.
- KOCNA, P, et al. Tissue transglutaminase-serology markers for coeliac disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002, vol. 40, no. 5, s. 485-92, ISSN 1434-6621. PMID: 12113293.
- WOLTERS, V, et al. Human tissue transglutaminase enzyme linked immunosorbent assay outperforms both the guinea pig based tissue transglutaminase assay and anti-endomysium antibodies when screening for coeliac disease. Eur J Pediatr. 2002, vol. 161, no. 5, s. 284-7, ISSN 0340-6199 (Print), 1432-1076 (Electronic). PMID: 12012226.
- HANSSON, T, et al. Recombinant human tissue transglutaminase for diagnosis and follow-up of childhood coeliac disease. Pediatr Res. 2002, vol. 51, no. 6, s. 700-5, ISSN 0031-3998 (Print), 1530-0447 (Electronic). PMID: 12032264.
- CLEMENTE, MG, et al. Antitissue transglutaminase antibodies outside celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002, vol. 34, no. 1, s. 31-4, ISSN 0277-2116 (Print), 1536-4801 (Electronic). PMID: 11753161.
- BARDELLA, MT, et al. Serological markers for coeliac disease: is it time to change?. Dig Liver Dis. 2001, vol. 33, no. 5, s. 426-31, ISSN 1590-8658 (Print), 1878-3562 (Electronic). PMID: 11529655.
- BASSO, D, et al. Role of anti-transglutaminase (anti-tTG), anti-gliadin, and anti-endomysium serum antibodies in diagnosing celiac disease: a comparison of four different commercial kits for anti-tTG determination. J Clin Lab Anal. 2001, vol. 15, no. 3, s. 112-5, ISSN 0887-8013 (Print), 1098-2825 (Electronic). PMID: 11344524.
- CHAN, AW, et al. Tissue transglutaminase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay as a screening test for celiac disease in pediatric patients. Pediatrics. 2001, vol. 107, no. 1, s. E8, ISSN 0031-4005 (Print), 1098-4275 (Electronic). PMID: 11134472.
- FABIANI, E, et al. The serum IgA class anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies in the diagnosis and follow up of coeliac disease. Results of an international multi-centre study. International Working Group on Eu-tTG. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001, vol. 3, no. 6, s. 659-65, ISSN 0954-691X (Print), 1473-5687 (Electronic). PMID: 11434591.
- LEON, F, et al. Anti-transglutaminase IgA ELISA: clinical potential and drawbacks in celiac disease diagnosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001, vol. 36, no. 8, s. 849-53, ISSN 0036-5521 (Print), 1502-7708 (Electronic). PMID: 11495081.
- KORDONOURI, O, et al. Autoantibodies to tissue transglutaminase are sensitive serological parameters for detecting silent coeliac disease in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2000, vol. 17, no. 6, s. 441-4, ISSN 0742-3071 (Print), 1464-5491 (Electronic). PMID: 10975212.