Trypsinogen v moči
Trypsinogen, trypsinogen aktivační peptid (TAP) a karboxypeptidázový aktivační peptid (CAPAP)[upravit | editovat zdroj]
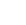
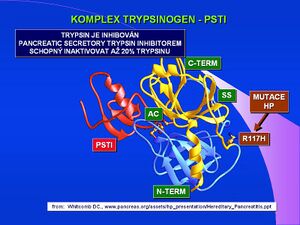
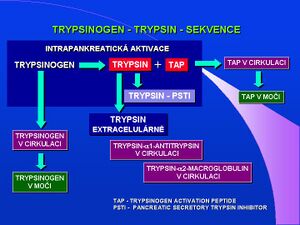
Trypsinogen (inaktivní forma, proenzym trypsinu) je produkován acinózními buňkami pankreatu ve dvou isoformách – trypsinogen-1 (katodický isoenzym, CT) a trypsinogen-2 (anodický isoenzym, AT). Zánětlivý proces při akutní pankreatitidě vede ke zvýšení hladiny v cirkulaci a trypsinogen-2 lze prokázat jak v séru tak v moči. Předčasná aktivace trypsinogenu v pankreatické tkáni vede ke spuštění aktivační kaskády, autodigesci a je významým patogenetickým faktorem akutní pankreatitidy. Laboratorně lze stanovovat imunoreaktivní, obě formy trypsinogenu (irAT, irCT) a jejich poměr v séru S-irAT/S-irCT nebo v moči U-irAT/U-irCT.
Klinika[upravit | editovat zdroj]
Klinicky je používána nejčastěji hladina trypsinogenu-2 v moči, hodnoty 5600–10 000 µg/l odpovídají těžké, závažné formě akutní pankreatitidy, hodnoty 130–890 µg/l pak střední až mírné formě AP. V moči stanovujeme také produkt konverze trypsinogenu na aktivní trypsin – trypsinogen aktivační peptid – TAP. Klinicky signifikantní je zvýšená hladina TAP pro posouzení závažnosti akutní pankreatitidy, kdy hodnoty TAP v moči nad 15 nmol/l detekují středně těžkou pankreatitidu, hodnoty nad 40 nmol/l těžkou formu onemocnění. Nejnovější studie se věnují stanovení aktivačního peptidu prokarboxypeptidázy B v séru nebo v moči. Aktivační peptid CAPAP je delší než ostatní peptidy uvolněné při aktivaci pankreatických proenzymů, je proto stabilnější a vhodnější pro laboratorní diagnostiku. Normální hladina CAPAP v séru metodou RIA je 0,8 nmol/l.
Odkazy[upravit | editovat zdroj]
Zdroj[upravit | editovat zdroj]
- se svolením autora převzato z KOCNA, Petr. GastroLab : MiniEncyklopedie laboratorních metod v gastroenterologii [online]. ©2002. Poslední revize 2011-01-08, [cit. 2011-03-04]. <http://www1.lf1.cuni.cz/~kocna/glab/glency1.htm>.
Použitá literatura[upravit | editovat zdroj]
- CARROLL, JK, et al. Acute pancreatitis: diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. American family physician. 2007, vol. 75, no. 10, s. 1513-20, ISSN 0002-838X (Print), 1532-0650 (Electronic). PMID: 17555143.
- SANKARALINGAM, S, et al. Use of the urinary trypsinogen-2 dip stick test in early diagnosis of pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Surgical endoscopy. 2007, vol. 21, no. 8, s. 1312-5, ISSN 0930-2794 (Print), 1432-2218 (Electronic). PMID: 17332967.
- JANG, T, et al. Point-of-care urine trypsinogen testing for the diagnosis of pancreatitis. Acad Emerg Med. 2007, vol. 14, no. 1, s. 29-34, ISSN 1069-6563 (Print), 1553-2712 (Electronic). PMID: 17119188.
- HILAL, MA, et al. Carboxypeptidase-B activation peptide, a marker of pancreatic acinar injury, but not L-selectin, a marker of neutrophil activation, predicts severity of acute pancreatitis. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology. 2007, vol. 22, no. 3, s. 349-54, ISSN 0815-9319 (Print), 1440-1746 (Electronic). PMID: 17295766.
- PETERSSON, U, et al. Characterization of immunoreactive trypsinogen activation peptide in urine in acute pancreatitis. JOP : Journal of the pancreas. 2006, vol. 7, no. 3, s. 274-82, ISSN 1590-8577 (Electronic). PMID: 16685108.
- AL-BAHRANI, AZ, et al. Clinical laboratory assessment of acute pancreatitis. Clin Chim Acta. 2005, vol. 362, no. 1-2, s. 26-48, ISSN 0009-8981 (Print), 1873-3492 (Electronic). PMID: 16024009.
- PAPACHRISTOU, GI, et al. Inflammatory markers of disease severity in acute pancreatitis. Clin Lab Med. 2005, vol. 25, no. 1, s. 17-37, ISSN 0272-2712 (Print), 1557-9832 (Electronic). PMID: 15749230.
- CHEN, YT, et al. Chen YT. Pancreas. 2005, vol. 30, no. 3, s. 243-7, ISSN 0885-3177 (Print), 1536-4828 (Electronic). PMID: 15782102.
- PEZZILLI, R, et al. Serum trypsinogen activation peptide in the assessment of the diagnosis and severity of acute pancreatic damage: a pilot study using a new determination technique. Pancreas. 2004, vol. 29, no. 4, s. 298-305, ISSN 0885-3177 (Print), 1536-4828 (Electronic). PMID: 15502646.
- LEMPINEM, M, et al. Trypsinogen-2 and trypsinogen activation peptide (TAP) in urine of patients with acute pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 2003, vol. 111, no. 2, s. 267-73, ISSN 0022-4804 (Print), 1095-8673 (Electronic). PMID: 12850473.
- MÜLLER, CA, et al. A study on the activation peptide released from procarboxypeptidase B (CAPAP) and anionic trypsinogen in patients with acute abdominal disorders of non-pancreatic origin. Pancreatology. 2003, vol. 3, no. 2, s. 149-55, ISSN 1424-3903 (Print), 1424-3911 (Electronic). PMID: 12748424.
- KYLÄNPÄÄ-BÄCK, ML, et al. Comparison of urine trypsinogen-2 test strip with serum lipase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002, vol. 49, no. 46, s. 1130-4, ISSN 0172-6390. PMID: 12143219.
- KYLÄNPÄÄ-BÄCK, ML, et al. Trypsin-based laboratory methods and carboxypeptidase activation peptide in acute pancreatitis. JOP. 2002, vol. 3, no. 2, s. 34-48, ISSN 1590-8577 (Electronic). PMID: 11884765.
- LEMPINEM, M, et al. Predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis by rapid measurement of trypsinogen-2 in urine. Clin Chem. 2001, vol. 47, no. 12, s. 2103-7, ISSN 0009-9147 (Print), 1530-8561 (Electronic). PMID: 11719473.
- PEZZILLI, R, et al. Clinical usefulness of the serum carboxypeptidase B activation peptide in acute pancreatitis. JOP. 2000, vol. 1, no. 3, s. 58-68, ISSN 1590-8577 (Electronic). PMID: 11854559.
- NEOPTOLEMOS, JP, et al. Early prediction of severity in acute pancreatitis by urinary trypsinogen activation peptide: a multicentre study. Lancet. 2000, vol. 355, no. 9219, s. 1955-60, ISSN 0140-6736 (Print), 1474-547X (Electronic). PMID: 10859041.
- KYLÄNPÄÄ-BÄCK, M, et al. Reliable screening for acute pancreatitis with rapid urine trypsinogen-2 test strip. Br J Surg. 2000, vol. 87, no. 1, s. 49-52, ISSN 0007-1323 (Print), 1365-2168 (Electronic). PMID: 10606910.
- KEMPPAINEN, E, et al. Time course profile of serum trypsinogen-2 and trypsin-2-alpha1-antitrypsin in patients with acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000, vol. 35, no. 11, s. 1216-20, ISSN 0036-5521 (Print), 1502-7708 (Electronic). PMID: 11145296.
- PETERSSON, U, et al. Different patterns in immunoreactive anionic and cationic trypsinogen in urine and serum in human acute pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol. 1999, vol. 25, no. 3, s. 165-70, ISSN 0169-4197 (Print). PMID: 10453418.