Detekce antigenu Helicobacter pylori ve stolici
Detekce antigenu Helicobacter pylori ve stolici je alternativou k dechovému testu, jako základní metoda průkazu infekce H. pylori. Metoda byla vypracována jako klasická ELISA, a provádí se na běžných mikrotitračních destičkách pro 96 vzorků. Vzorek stolice je připraven v koncentraci 200 mg/ml a centrifugován 5 minut při 7000×g. Další postup je běžnou ELISA technikou, s tetrametylbenzidinem jako substrátem a fotometrickým vyhodnocením při 450 nm. Existuje několik modifikací ELISA metody, které dosahují specificity i senzitivity 98 %. Původní metoda (HpSAg) používala polyklonální protilátky, novější metody s monoklonální protilátkou vykazují vyšší diagnostické parametry. Z hlediska odběru vzorku je metoda pro pacienta nenáročná, laboratoře mají odběrové nádobky s plastikovým jádrem v podobě lžičky, kterou je vzorek stolice odebrán a uzavřen. Vzorky stolice je možno uchovávat při –20 °C i několik měsíců.
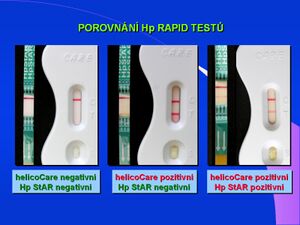
V poslední době se objevují i rychlé rapid testy na imunochromatografickém detekčním principu, určené pro jednotlivé vyšetření. Spolehlivost těchto rapid testů je však ve srovnání s ELISA metodou nižší, výsledky rapid testů mohou být ovlivněny odběrem stolice.
Odkazy[upravit | editovat zdroj]
Zdroj[upravit | editovat zdroj]
- se svolením autora převzato z KOCNA, Petr. GastroLab : MiniEncyklopedie laboratorních metod v gastroenterologii [online]. ©2002. Poslední revize 2011-01-08, [cit. 2011-03-04]. <http://www1.lf1.cuni.cz/~kocna/glab/glency1.htm>.
Použitá literatura[upravit | editovat zdroj]
- ZAMBON, CF, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection: simplified 13C-urea breath test, stool antigen testing, or DNA PCR in human feces in a clinical laboratory setting?. Clinical biochemistry [online]. 2004, vol. 37, no. 4, s. 261-267, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15003727?dopt=Abstract>. ISSN 0009-9120, eISSN 1873-2933. PMID: 15003727.
- TREVISANI, L, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a rapid fecal test to confirm H pylori eradication after therapy: prospective comparison with a laboratory stool test. World journal of gastroenterology [online]. 2007, vol. 13, no. 33, s. 4484-4488, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17724805?ordinalpos=31&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum>. ISSN 1007-9327. PMID: 17724805.
- SCHWARZER, A, et al. Evaluation of a novel rapid one-step monoclonal chromatographic immunoassay for detection of Helicobacter pylori in stool from children. European journal of clinical microbiology & infectious diseases [online]. 2007, vol. 26, no. 7, s. 475-480, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=pubmed&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=17554570&ordinalpos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum>. ISSN 0934-9723, eISSN 1435-4373. PMID: 17554570.
- STRAY-PEDERSEN, A, et al. Detection rate of Helicobacter pylori stool antigen in newborn infants and small children. Journal of perinatal medicine [online]. 2007, vol. 35, no. 2, s. 155-158, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17343545?dopt=AbstractPlus>. ISSN 0300-5577, eISSN 1619-3997. PMID: 17343545.
- DOMÍNGUEZ, J, et al. Comparison of a monoclonal with a polyclonal antibody-based enzyme immunoassay stool test in diagnosing Helicobacter pylori infection before and after eradication therapy. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics [online]. 2006, vol. 23, no. 12, s. 1735-1740, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16817917?dopt=AbstractPlus>. ISSN 0269-2813, eISSN 1365-2036. PMID: 16817917.
- HOOTON, C, et al. Comparison of three stool antigen assays with the 13C- urea breath test for the primary diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and monitoring treatment outcome. European journal of gastroenterology & hepatology [online]. 2006, vol. 18, no. 6, s. 595-599, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16702847?dopt=Abstract>. ISSN 0954-691X, eISSN 1473-5687. PMID: 16702847.
- HAUSER, B, et al. Multiple-step polyclonal versus one-step monoclonal enzyme immunoassay in the detection of Helicobacter pylori antigen in the stools of children. Acta paediatrica [online]. 2006, vol. 95, no. 3, s. 297-301, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16497639?dopt=Abstract>. ISSN 0001-656X. PMID: 16497639.
- ANTOS, D, et al. Evaluation of a novel rapid one-step immunochromatographic assay for detection of monoclonal Helicobacter pylori antigen in stool samples from children. European journal of clinical microbiology [online]. 2005, vol. 43, no. 6, s. 2598-2601, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15956370>. ISSN 0722-2211. PMID: 15956370.
- GATTA, L, et al. A rapid immunochromatographic assay for Helicobacter pylori in stool before and after treatment. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics [online]. 2004, vol. 20, no. 4, s. 469-474, dostupné také z <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15298642?dopt=Abstract>. ISSN 0269-2813, eISSN 1365-2036. PMID: 15298642.
- NAKATA, H, et al. Immunological rapid urease test using monoclonal antibody for Helicobacter pylori. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2004, roč. 19, vol. 9, s. 970–974, ISSN 08159319. PMID: 15304111.
- LEODOLTER, A, et al. Evaluation of a near-patient fecal antigen test for the assessment of Helicobacter pylori status. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004, vol. 48, no. 2, s. 145-7, ISSN 0732-8893 (Print), 1879-0070 (Electronic). PMID: 14972385.
- KOLETZKO, S, et al. Evaluation of a novel monoclonal enzyme immunoassay for detection of Helicobacter pylori antigen in stool from children. Gut. 2003, vol. 52, no. 6, s. 804-6, ISSN 0017-5749 (Print), 1468-3288 (Electronic). PMID: 12740334.
- ANDREWS, J, et al. Comparison of three stool antigen tests for Helicobacter pylori detection. J Clin Pathol. 2003, vol. 56, no. 10, s. 769-71, ISSN 0021-9746 (Print), 1472-4146 (Electronic). PMID: 14514781.
- KATO, S, et al. Accuracy of the stool antigen test for the diagnosis of childhood Helicobacter pylori infection: a multicenter Japanese study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003, vol. 98, no. 2, s. 296-300, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 12591044.
- LEODOLTER, A, et al. Comparison of two enzyme immunoassays for the assessment of Helicobacter pylori status in stool specimens after eradication therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002, vol. 97, no. 7, s. 1682-6, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 12135018.
- CHANG, MC, et al. Quantitative correlation of Helicobacter pylori stool antigen (HpSA) test with 13C-urea breath test (13C-UBT) by the updated Sydney grading system of gastritis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002, vol. 49, no. 44, s. 576-9, ISSN 0172-6390 (Print). PMID: 11995501.
- ODAKA, T, et al. Evaluation of the Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test for monitoring eradication therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002, vol. 97, no. 3, s. 594-9, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 11922552.
- KONSTANTOPOULOS, N, et al. Evaluation of the Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test (HpSA) for detection of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001, vol. 96, no. 3, s. 677-83, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 11280533.
- VAN DOORN, OJ, et al. Helicobacter pylori Stool Antigen test: a reliable non-invasive test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001, vol. 13, no. 9, s. 1061-5, ISSN 0954-691X (Print), 1473-5687 (Electronic). PMID: 11564956.
- LEODOLTER, A, et al. Validity of a Helicobacter pylori stool antigen assay for the assessment of H. pylori status following eradication therapy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001, vol. 13, no. 6, s. 673-6, ISSN 0954-691X (Print), 1473-5687 (Electronic). PMID: 11434593.
- ODERDA, G, et al. Usefulness of Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test to monitor response to eradication treatment in children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001, vol. 15, no. 2, s. 203-6, ISSN 0269-2813 (Print), 1365-2036 (Electronic). PMID: 11148438.
- VAIRA, D, et al. Noninvasive antigen-based assay for assessing Helicobacter pylori eradication: a European multicenter study. The European Helicobacter pylori HpSA Study Group. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000, vol. 95, no. 4, s. 925-9, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 10763939.